Flipping Perspectives: STEAM Education and the Flipped Classroom
Revolutionizing Learning: The Fusion of STEAM Education and the Flipped Classroom
In the ever-evolving landscape of education, the integration of STEAM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Arts, and Mathematics) principles with the flipped classroom model has emerged as a dynamic strategy. This article explores the synergies between STEAM education and the flipped classroom, unveiling how this innovative approach transforms traditional learning paradigms.
Understanding the Flipped Classroom Model
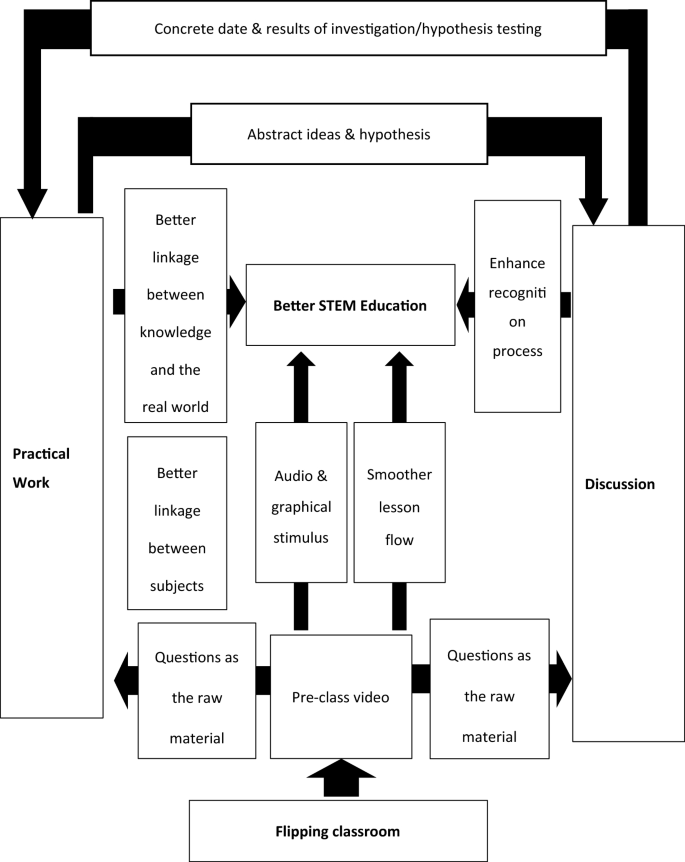
The flipped classroom model flips the traditional sequence of learning. Instead of receiving new content during class time, students engage with instructional materials, such as videos or readings, independently before class. Classroom time is then dedicated to applying and reinforcing the concepts through collaborative activities, discussions, and problem-solving.
Empowering Self-Directed Learning in STEAM
STEAM education emphasizes hands-on and exploratory learning. The flipped classroom aligns seamlessly with this philosophy by placing the responsibility of absorbing foundational knowledge on the students outside of class. This approach fosters self-directed learning, encouraging students to delve into STEAM subjects at their own pace and revisit materials as needed.
Maximizing Classroom Time for Application
The flipped classroom liberates precious class time for application and interaction. In STEAM subjects, where experimentation, group projects, and problem-solving are paramount, this model provides the ideal environment. Classrooms become dynamic hubs for collaborative exploration, allowing students to apply theoretical knowledge to real-world scenarios with guidance from educators.
Incorporating Multimodal Learning Resources
STEAM subjects often involve complex concepts that benefit from multiple modes of presentation. The flipped classroom allows educators to curate a variety of multimodal learning resources – from videos and simulations to articles and interactive platforms. This diverse array of resources accommodates different learning styles, ensuring that each student can access information in the way that suits them best.
Enhancing Accessibility in STEAM Education
Accessibility is a cornerstone of equitable education. The flipped classroom, by providing pre-recorded materials that students can access at any time, ensures that learning is not confined to the traditional classroom schedule. This flexibility accommodates diverse student needs, including those who may require additional time for understanding complex STEAM concepts.
Facilitating Peer Collaboration and Problem-Solving
Collaboration is integral to both STEAM education and the flipped classroom model. During class time, students can engage in collaborative projects, share insights, and collectively solve problems. This fosters a sense of community and teamwork, skills crucial in STEAM fields where interdisciplinary collaboration is often the key to innovative solutions.
Real-Time Feedback and Assessment
The flipped classroom model allows educators to provide real-time feedback on students’ application of knowledge. In STEAM education, where experimentation and problem-solving are central, immediate feedback is invaluable. Educators can address misconceptions promptly, guiding students toward a deeper understanding of STEAM concepts.
Encouraging Active Participation in Discussions
Classroom discussions play a pivotal role in STEAM education. The flipped model encourages active participation, as students enter the classroom armed with a foundational understanding. This engagement leads to more meaningful discussions, where students can explore advanced topics, share insights, and collectively delve deeper into STEAM subjects.
Addressing Challenges and Providing Support
The flipped classroom model allows educators to identify individual challenges more effectively. In STEAM education, where students may encounter complex mathematical or scientific concepts, personalized support is crucial. Educators can use class time to address specific challenges, providing targeted assistance and ensuring that every student progresses in their STEAM learning journey.
Embracing Continuous Improvement in STEAM Learning
To explore more about the transformative fusion of STEAM education and the flipped classroom, visit essayoutlinewritingideas.com. The dynamic interaction between self-directed learning, collaborative exploration, and real-time feedback positions the flipped classroom as a catalyst for continuous improvement in STEAM education. As we continue to flip perspectives and reimagine the educational landscape, the fusion of STEAM and the flipped classroom promises a future of innovative and effective learning experiences.



